Imagine you're running a critical operation, and suddenly, the power goes out. Your servers crash, your data is lost, and your operations grind to a halt. This downtime is costly and frustrating.
A UPS (Uninterruptible Power Supply) battery is the core component of a UPS system that provides instant, temporary power during a power outage or voltage fluctuation. It acts as an emergency power source, ensuring your critical equipment continues to run, preventing data loss and hardware damage.

As a manufacturer of high-performance batteries, we understand that power continuity is not a luxury; it's a necessity. A UPS battery is your first line of defense against power disturbances. It's the silent guardian that keeps your business running when the grid fails. But not all UPS batteries are the same, and understanding the differences is key to reliable protection.
How Does a UPS Battery Protect My Equipment?
You've invested heavily in servers, medical equipment, or control systems. A sudden power spike or blackout can destroy them in an instant, leading to expensive repairs and catastrophic data loss.
A UPS battery protects equipment in two main ways: it provides immediate backup power during an outage and it conditions incoming power, smoothing out dangerous voltage sags and surges to deliver clean, stable electricity to your connected devices.

Think of a UPS battery as both a bodyguard and a water filter for your electricity.
1. Instant Backup Power
When the main power supply fails, the UPS system instantly switches to battery power. This transition happens in milliseconds, so your devices don't even notice the interruption. This gives you a critical window of time to either save your work and perform a graceful shutdown or for a backup generator to kick in. This function is the primary role of a UPS and is essential for:
- Data Centers: Preventing server crashes and data corruption.
- Hospitals: Keeping life-support and diagnostic equipment running.
- Industrial Controls: Averting production line stoppages.
2. Power Conditioning
The electricity from the grid is not always "clean." It can be subject to sags (dips in voltage), surges (spikes in voltage), and other noise. These fluctuations can slowly damage sensitive electronic components. A UPS system constantly filters this incoming power, using the battery to supplement voltage during sags and absorbing excess energy during surges. It ensures your equipment always receives a stable, pure sine wave of electricity, significantly extending its lifespan.
What Types of Batteries Are Used in UPS Systems?
You need a reliable UPS system, but you're faced with a choice between different battery technologies. One is a proven, cost-effective standard, while the other is a modern, high-performance option. Choosing the wrong one could mean higher long-term costs or shorter backup times.
The two main types of UPS batteries are Valve-Regulated Lead-Acid (VRLA) and Lithium-ion (Li-ion). VRLA is the traditional, cost-effective choice, while Li-ion offers a longer lifespan, smaller footprint, and better performance at a higher initial cost.
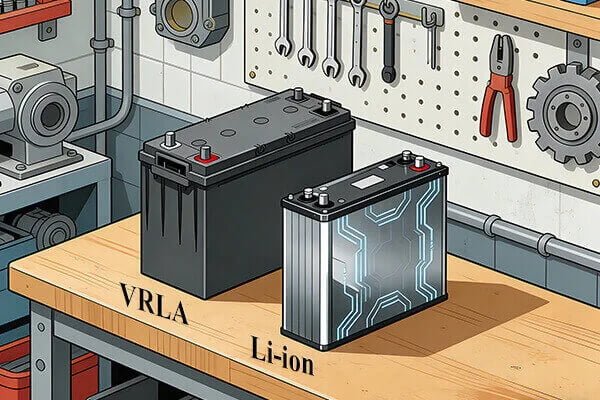
The choice between these two technologies depends on your budget, application, and total cost of ownership considerations.
| Feature | Valve-Regulated Lead-Acid (VRLA) | Lithium-ion (Li-ion) |
|---|---|---|
| Typical Lifespan | 3–5 years | 8–10+ years |
| Size & Weight | Larger and heavier | Smaller and lighter (higher energy density) |
| Upfront Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Total Cost of Ownership | Higher (due to frequent replacements) | Lower (fewer replacements over life) |
| Maintenance | Minimal, but sensitive to temperature | Virtually maintenance-free |
| Best For | Cost-sensitive applications, small offices, personal use. | Data centers, medical facilities, critical infrastructure, long-term deployments. |
Why Lithium-ion is the Future for Critical UPS
At KKLIPO, while we specialize in Li-ion and LiPo batteries for mobile applications like drones, the same principles apply to stationary power. Lithium-ion technology is rapidly becoming the preferred choice for modern data centers and critical applications. Why? Because the total cost of ownership is significantly lower. A Li-ion UPS battery might last twice as long as its VRLA counterpart, meaning fewer replacement cycles, less labor cost, and reduced risk during maintenance. Its smaller footprint also frees up valuable rack space in a crowded data center.
What Key Factors Should I Consider When Choosing a UPS Battery?
You know you need a UPS battery, but how do you select the right one? Choosing based on price alone can lead to inadequate backup time or premature failure. It's a technical decision that requires careful thought.
When choosing a UPS battery, the most critical factors are capacity (Ah), which determines runtime; voltage, which must match the UPS system; and expected lifespan, which impacts the total cost of ownership. You must align these with your specific load and backup time requirements.

Selecting the right battery is a balancing act. Here’s a breakdown to guide your decision:
1. Capacity (Ah) and Load (Watts)
Capacity, measured in Amp-hours (Ah), is the "size of the fuel tank." The higher the capacity, the longer the battery can power your equipment. You must calculate the total power consumption (in Watts) of all connected devices to determine the required battery capacity for your desired runtime. For instance, a 1000W load will drain a battery much faster than a 100W load.
2. Voltage (V)
The battery voltage must match the specifications of your UPS system. UPS systems are designed to work with a specific voltage, typically configured by connecting multiple 12V batteries in series (e.g., 24V, 48V, 96V). Using the wrong voltage can damage the UPS and the connected equipment.
3. Lifespan and Environment
Battery lifespan is heavily influenced by its operating environment. The ideal temperature for most UPS batteries is around 20-25°C (68-77°F). Every 8-10°C increase above this can cut the battery's lifespan in half. When procuring batteries, especially for harsh environments, consider solutions with better temperature tolerance or ensure adequate climate control.
Conclusion
A UPS battery is your critical defense against power outages, providing backup power and clean electricity. Choose between lead-acid and lithium-ion based on lifespan and budget, ensuring capacity and voltage match your system's needs.